逆境模拟及植物生长监测系统 Plantarray

逆境模拟及植物生长监测系统是一套高通量,以植物生理学为基础的高精度表型系统,可以完成整个植物生长周期中不同环境下的SPAC因子的测量。连续不间断的获取阵列内所有植物的监测数据,实时监控和及时调整每个培养容器中的土壤条件,包含土壤水分、盐分。

Israeli Center of Research Excellence facility in Rehovot
逆境模拟及植物生长监测系统的主要优点:
生理学特征的监测和数据高通量分析,如生长速率、蒸腾速率、水分利用率、气孔导度等特征;
连续控制不同的土壤和水分环境(如干旱、盐分或化学物质);
理想的实验平台:
全自动;
均一检测;
适用于不同类型植物;
精确测量;
非破坏性;
实现随机分组实验设计;
3-4周的实验相当于4-6个月的人工工作;
操作简单,维护费用几可忽略;
灵活的设计能够满足任何温室中不同方面的科学研究需求。
实时统计分析-为了数据的可靠快速分析,提供多阶乘ANOVA或配对T检验;
实验目的-在实验运行中为了确保处理的效果可以获取优化的实验参数;
快速定量选择-提供植物对于不同环境需求生理反应的评级和评分的简况;
复杂实验通过简要图像呈现生理参数与环境条件的空间和时间关系,显示趋势、异常和比率。
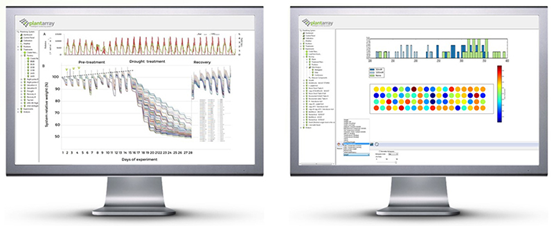
逆境模拟及植物生长监测系统的应用领域:
非生物逆境胁迫研究,比如:干旱、淹水、营养、有毒物质等胁迫研究;
在农作物、蔬菜、树木、YY植物、燃料作物等方面的育种研究;
根系的土壤穿透力、水通量研究;
生物激素与养分研究;
生理生态学研究等。
测量参数:
直接测量参数: | ||
重量 | 空气湿度 | 空气温度 |
辐射(PAR) | 气压 | 土壤水分 |
土壤电导率 | 土壤温度 | 日蒸腾 |
计算参数: | ||
植物生物量增益 | 日蒸腾 | 水分利用效率 |
气孔导度 | 抗胁迫因子 | 水分相对含量 |
根穿透力 | 根系水通量 | VPD |
逆境模拟及植物生长监测系统的技术参数:
l PIU单元含有3个数字通道、1个模拟通道、1个称重式蒸渗仪通道,所有的传感器可以同时连续工作;
l 德国高精度称重模块,ZD测重量50kg(测量范围根据具体配置而定),测量精确度±0.02%称重量;
l 植物生长容器满足多种植物的生长需求,容积1.5-60L,具有防漏水、溅水设计;
l 可以根据植物生长时间或生长容器重量选择灌溉模式,灌溉系统采用以色列JZ的滴灌系统控制,能够精确的控制浇水、施肥或施加生物激素的量;
l 土壤类、气象类传感器选择美国高精度传感器测量土壤含水量、温度、电导率,空气温湿度、PAR、气压等参数;
应用案例
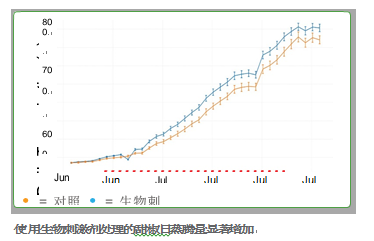
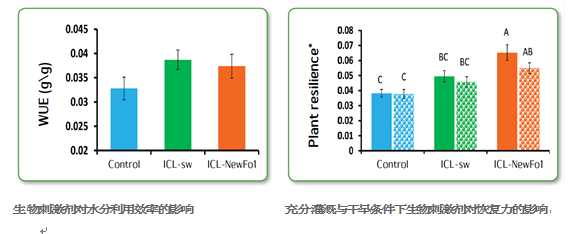

代表文献:
1. Xinyi Wu. et al. Unraveling the Genetic Architecture of Two Complex, Stomata-Related Drought-Responsive Traits by High-Throughput Physiological Phenotyping and GWAS in Cowpea. Frontiers in Genetics, 743758(2021)
2. AK Pandey. et al. Functional physiological phenotyping with functional mapping: a general framework to bridge the phenotype-genotype gap in plant physiology. iScience, 102846(2021).
3. Yanwei Li. et al. High-Throughput physiology-based stress response phenotyping: Advantages, applications and prospective in horticultural plants. Horticultural Plant Journal (2020)
4. Weksler, S. et al. A Hyperspectral-Physiological Phenomics System: Measuring Diurnal Transpiration Rates and Diurnal Reflectance. Remote Sensing 12, 1493 (2020).
5. Illouz-Eliaz, N. et al. Mutations in the tomato gibberellin receptors suppress xylem proliferation and reduce water loss under water-deficit conditions. Journal of Experimental Botany (2020).
6. Dalal, A. et al. A High Throughput Gravimetric Phenotyping Platform for Real Time Physiological Screening of Plant Environment Dynamic Responses. bioRxiv (2020).
7 . Yaaran, A., Negin, B. & Moshelion, M. Role of guard-cell ABA in determining steady-state stomatal aperture and prompt vapor-pressure-deficit response. Plant Science 281, 31-40, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.12.027 (2019).
8 . Illouz-Eliaz, N. et al. Multiple Gibberellin Receptors Contribute to Phenotypic Stability under Changing Environments. The Plant Cell 31, 1506, doi:10.1105/tpc.19.00235 (2019).
9 . Gosa, S. C., Lupo, Y. & Moshelion, M. Quantitative and comparative analysis of whole-plant performance for functional physiological traits phenotyping: New tools to support pre-breeding and plant stress physiology studies. Plant Science 282, 49-59, doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.05.008 (2019).
10 . Dalal, A. et al. Dynamic Physiological Phenotyping of Drought-stressed Pepper Plants Treated with'Productivity-Enhancing’and'Survivability-Enhancing’Biostimulants. Frontiers in Plant Science 10, 905 (2019).
11 . Dalal, A. et al. A High-Throughput Physiological Functional Phenotyping System for Time-and Cost-Effective Screening of Potential Biostimulants. bioRxiv, 525592 (2019).
12 . Galkin, E. et al. Risk‐management strategies and transpiration rates of wild barley in uncertain environments. Physiologia plantarum (2018).
13 . Yaaran, A., Negin, B. & Moshelion, M. Role of guard-cell ABA in determining maximal stomatal aperture and prompt vapor-pressure-deficit response. bioRxiv, 218719 (2017).
14 . Nir, I. et al. The tomato DELLA protein PROCERA acts in guard cells to promote stomatal closure. The Plant Cell, tpc. 00542.02017 (2017).
以色列 Plant-Ditech
上海泽泉科技股份有限公司
仪器网(yiqi.com)--仪器行业网络宣传传媒