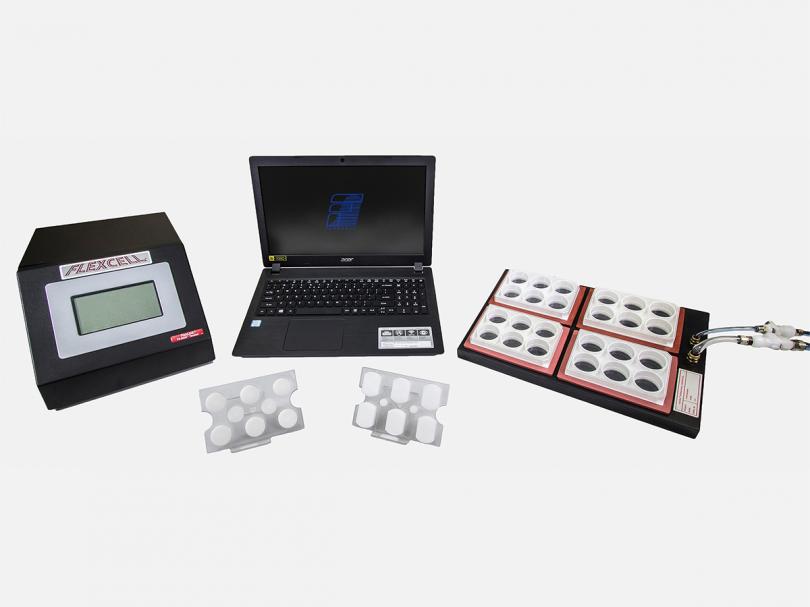

微流控张力细胞拉伸生物系统一款通过电脑控制的生物反应器,使用真空压力和正气压力可对体外培养的细胞施加循环或静态应变。该系统可应用于分析各种细胞培养应用(例如肌肉、心脏、肺、血管、皮肤、肌腱、韧带、软骨和骨骼等)在拉伸负荷下的生物化学变化。此外,该张力系统还可与 UniFlex(单轴应变)、BioFlex、HT BioFlex(等双轴应变)、Tissue Train 和 CellSoft BioFlex 培养板配合使用。
微流控张力系统的工作原理
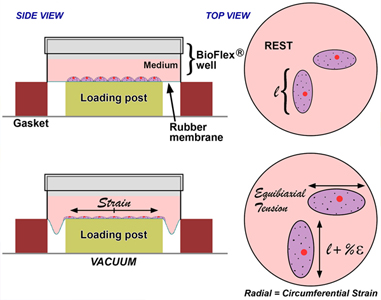
微流控细胞拉伸生物反应器系统非常适合使用机械应变刺激细胞培养中的细胞。 使用我们的气动拉伸协议系统而不是电机驱动或电气系统,您可以避免任何混杂的振动应变、电场干扰 (E) 或磁场干扰 (B)。
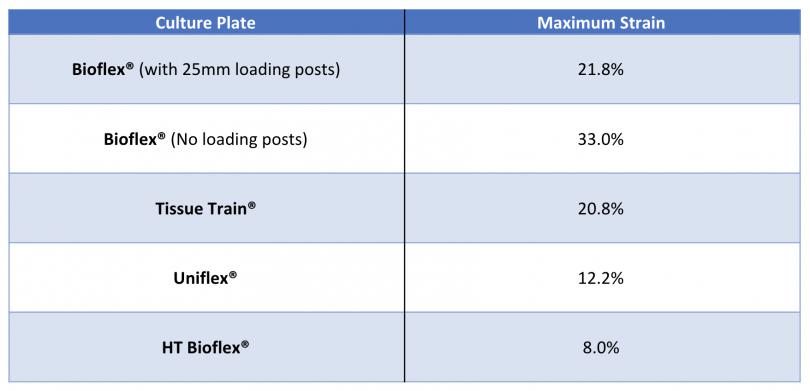
使用 Bioflex 培养板的 Flexcell 张力系统应用等双轴应变
微流控张力细胞拉伸生物系统FX-6000T的优点:
1)对3D或单层生长的细胞应用自定义的、受控的、静态的或循环的变形压力;
2)允许用户在体外模拟体内组织应变和频率变化
3)先进的数字阀为特定应变区域自动调节真空压力和正气压力
4)模拟来自肌肉、肺、心脏、血管、皮肤、肌腱、韧带、软骨和骨骼的细胞的体内条件;
5)FlexSoft FX-6000操作软件允许在一个方案中对多个频率、幅度和波形变化进行编程;
6)兼容 Windows 10系统
7)使用带有圆柱形加载柱的 Bioflex 培养板施加等双轴应变
8)使用带有 Arctangle 加载柱的 Uniflex 培养板来施加单轴应变
9)通过移除加载件实现梯度应变或无约束膨胀
10)使用 1 个 FX-6000T 张力系统驱动多达 4 个 Flexlink 控制器
11)控制器可用压力波形:静态、正弦、心脏刺激、三角形、方形和自定义
参考文献
Altalhi W, Sun X, Sivak JM, Husain M, Nunes SS. Diabetes impairs arterio-venous specification in engineered vascular tissues in a perivascular cell recruitment-dependent manner. Biomaterials 119:23-32, 2017.
Cevallos M, Riha GM, Wang X, Yang H, Yan S, Li M, Chai H, Yao Q, Chen C. Cyclic strain induces expression of specific smooth muscle cell markers in human endothelial cells. Differentiation 74(9-10):552-561, 2006.
Freese C, Anspach L, Deller RC, Richards SJ, Gibson MI, Kirkpatrick CJ, Unger RE. Gold nanoparticle interactions with endothelial cells cultured under physiological conditions. Biomater Sci 5(4):707-717, 2017.
Gao M, Wu S, Ji J, Zhang J, Liu Q, Yue Y, Liu L, Liu X, Liu W. The influence of actin depolymerization induced by Cytochalasin D and mechanical stretch on interleukin-8 expression and JNK phosphorylation levels in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. BMC Ophthalmol 17(1):43, 2017.
Harris C, Rushwan S, Wang W, Thorpe S, Thompson C, Peacock J, Knight M, Gooptu B, Greenough A. P07 Interleukin response to cyclical mechanical stretch with models of different neonatal ventilation modes. Archives of Disease in Childhood 102:A4, 2017.
Freeman SA, Christian S, Austin P, Iu I, Graves ML, Huang L, Tang S, Coombs D, Gold MR, Roskelley CD. Applied stretch initiates directional invasion through the action of Rap1 GTPase as a tension sensor. J Cell Sci 130(1):152-163, 2017.
Glaeser JD, Salehi K, Kanim LE, NaPier Z, Kropf MA, Cuellar J, Sheyn D, Bae HW. Treatment with the NFkB inhibitor reduces overloading-induced MMP expression in human nucleus pulposus cells. The Spine Journal 17(10):S127, 2017.
Klymenko Y, Wates RB, Weiss-Bika H, Lombard R,Liu Y, Campbell L, Kim O, Wagner D, Ravosa MJ, Stack MS. Modeling the effect of ascites-induced compression on ovarian cancer multicellular aggregates. Dis Model Mech.2018 Sep 25; 11 (9).
Ackermann P, Schizas N, Bring D, Li J, Andersson T, Fahlgren A, Aspenberg P. Compression therapy promotes tissue repair and biomechanical properties during immobilization. J Bone Joint Surg Br 94B (Supp XXXVII) 89, 2012.
泰初科技(天津)有限公司
仪器网(yiqi.com)--仪器行业网络宣传传媒